معلومات المقرر

CHAPTER 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS
This chapter is a general introduction to the structure of matter, which contains basic notions and definitions for the acquisition of basic formalisms in chemistry, particularly within matter describing the atom, atomic mass unit, different types transformations, concentrations and different types of solutions. CHAPTER 2: MAIN CONSTITUENTS OF MATTER
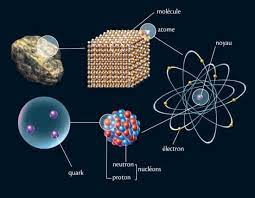
his chapter is devoted to the main constituents of matter (electron, proton and neutron) taking into account the following Experiments: - Crookes experiment and characteristics of cathode radiation.- Experiment of J.J.Thomson: Determination of the ratio |e|/m. - Millikan experiment: Determination of the charge |e| of the electron and deduction of its mass. - Goldstein experiment: demonstration of the positive charge of the nucleus.- Rutherford experiment: demonstration of the proton existing in the nucleus.- Chadwick experiment: demonstration of the neutron existing in the nucleus.CHAPTER 3:RADIOACTIVITY IS NUCLEAR REACTIONS
Chapter 3 deals with natural radioactivity (α, β, and γ radiation), artificial radioactivity and nuclear reactions. This chapter also deals with the energetic and kinetic aspect of radioactive decay with applications in the military, medicine and biological fields.
CHAPTER 4: Bohr model
his chapter presents the classic classical model of the atom (Rutherford model) to know the electronic structure of the atom. This model is modified by Bohr who introduces the notion of quantification. So, this chapter deals more with the Bohr model. CHAPTER 5: MODEL BASED ON WAVE MECHANICS
Inadequacies of the Bohr model, we need a real model that describes the electronic structure of the atom, this is the quantum model. Chapter 5 deals with the quantum (wave) model of the atom. This model based on the Louis De Broglie relation, uncertainty principle, Schrödinger equation, wave functions, atomic orbitals, etc.). CHAPTER 6: Electronic configurations
The chapter is devoted to the Electronic configurations of polyelectronic atoms. The Chapter deals with the filling rules to know the electronic configurations of atoms and their physico-chemical properties.
CHAPTER 7: Periodic classification of chemical elements
The chapter deals with the periodic classification of chemical elements in a periodic table by studying some characteristics concerning the atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity and electronegativity.
CHAPTER 8: Chemical bond
The chapter presents the chemical bond model. This chapter covers the following points:Lewis model - Covalent bond - Molecular orbitals - σ bond and П bond - Energy diagram of molecules, bond order - Ionic bond - Partial ionic character - Hybridizations - Geometry of molecules, Gillespie method.- معلم: BOUACHA Samir
