Java Language
Aperçu des sections
-
-
Instructor : Dr. Brik mourad
Email : Mourad.brik@univ-msila.dz
Hourly Volume : 37h30
Weekly Hours : C : 1h30 WP : 1h
Coefficient: 2
Credits : 3
Evaluation method : Exam: 60% Continuous assessment: 40%;Availability : - At the department: monday from 9 a.m. and Thursday from 8 a.m. - By email: I undertake to respond by email within 24 hours of receipt of the messag. -
Recommended Prerequisites:
- C/C++ Programming Language
- Object-Oriented Programming
Objectives:
This subject allows the student to reach a significant level in Java programming language, enabling them to address this aspect of modern technology
-
Page
1. Java Introduction
1.1.Java Virtual Machine
1.2.JVM, JRE and JDK
1.3.Exist Java Platforms
1.4.Key Difference and similarity Between Java and C#
1.5.Key Difference between Java and C++
1.6.Exercises
2. Basic concept
2.1. Primitive type in java
2.2. Control Structures
2.2.1. Blocks
2.2.2. Conditional Control Structure
2.2.2.1. if, else Statement
2.2.2.2. If statement
2.2.2.3. if else statement
2.2.3. Using if with multiple statements
2.2.4. Switch, case, default, break
2.3. Repetition Control Structure (Loops)
2.3.1. While statement
2.3.2. The do-while Statement
2.3.4. For statement
2.4. Using Break and Continue in java
2.5. Array of primitive type
2.5.1. Array Creation
2.5.2. Accessing Array Elements
2.6. Integrated arithmetic functions
2.7. Java basic operators
2.8. Exercises
3.1. Object-Oriented Programming (O.O.P)
3.2. Declaring Classes
3.3. Variables and method instance
3.3.1. Objects and instances
3.3.2. Java Methods
3.3.3. Modifiers
3.3.4. Return value
3.3.5. Parameters
3.4. Static Methods and Variables
3.5. Method Overloading
3.6. Java access rights
3.7. Encapsulation in java
3.8. Java Contructor and Destructor
3.9. Accessor and mutator
3.9.1. Accessor
3.9.2. Mutator
3.10. Array of objects in java
4.1. Inheritance
4.1.1. Syntax
4.2. Inheritance and constructor
4.2.1. Invoking Superclass Constructors
4.2.2. Calling Superclass Methods
4.3. Polymorphism
4.3.1. Method overloading
4.3.2. Method Overriding
4.4. Abstract Class and method
4.5. Interface
4.6. Overload (method surcharging)
4.7. Modifiers
5. Integrated Generic data structure in java
5.1.1 Interfaces and implementation
5.1.2. Generic types in Java
5.1.2.1. Set interface
5.1.2.1.1. HashSet
5.1.2.1.2. LinkedHashSet
5.1.2.3. List
5.1.2.3.1 ArrayList
5.1.2.4. Map
5.1.2.5. Queue
5.2. Collection Algorithms
5.2.1. Fill
5.2.3. Sort
5.2.4. Shuffle
5.2.5. Reverse Order
5.2.6. Binary Search
5.3. Collections’ iterating
5.3.1. For-each
5.3.2. Iterator
5.3.3. Massive operations in Java
6.1. Standard Java library API
6.2. Java Natives Interface (JNI)
6.3. AWT and SWINGx library
6.3.1. AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
6.3.2. Swingx
-
Chat
-
DevoirAs a first homework, students are invited to do the following :
- Install the latest version of java virtual machine (JVM)
link: https://www.java.com/en/download/
- Download the eclipse editor from: https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/
-
-
-
Fichier
JVM, JRE and JDK
.Exist Java Platforms
Key Difference and similarity Between Java and C#
Key Difference between Java and C++
-
Devoir
- Is C++ a compiler? Cite two advantage of an interpreter?
- · What is the main purpose of JVM?
- · What is JDK? Is eclipse a JRE?
- · Cite two features of java program vs c# program
-
-
-
Fichier
2.1. Primitive type in java
2.2. Control Structures
2.2.1. Blocks
2.2.2. Conditional Control Structure
2.2.2.1. if, else Statement
2.2.2.2. If statement
2.2.2.3. if else statement
2.2.3. Using if with multiple statements
2.2.4. Switch, case, default, break
2.3. Repetition Control Structure (Loops)
2.3.1. While statement
2.3.2. The do-while Statement
2.3.4. For statement
2.4. Using Break and Continue in java
2.5. Array of primitive type
2.5.1. Array Creation
2.5.2. Accessing Array Elements
2.6. Integrated arithmetic functions
2.7. Java basic operators
-
- How does write do-while loop with while-do loop?
- · Cite the primitive types and its range of values?
- · What is an array of primitive type? Is it an object?
-
-
-
Fichier
3. Classes and Objects
3.1. Object-Oriented Programming (O.O.P)
3.2. Declaring Classes
3.3. Variables and method instance
3.3.1. Objects and instances
3.3.2. Java Methods
3.3.3. Modifiers
3.3.4. Return value
3.3.5. Parameters
3.4. Static Methods and Variables
3.5. Method Overloading
3.6. Java access rights
3.7. Encapsulation in java
3.8. Java Contructor and Destructor
3.9. Accessor and mutator
3.9.1. Accessor
3.9.2. Mutator
3.10. Array of objects in java
-
Devoir
- Write a Java program to create a class called "Shape" with a name and color attribute. Create two instances of the "shape" class, set their attributes using the constructor and modify the attributes using the setter methods and print the updated values.
- Write a Java program to create a class called "Book" with attributes for title, author, and ISBN, and methods to add and remove books from a collection
- Write a Java program to create a class called "Employee" with a name, salary, and hire date attributes, and a method to calculate years of service
-
-
-
4. Inheritance, polymorphism and Abstract class
4.1. Inheritance
4.1.1. Syntax
4.2. Inheritance and constructor
4.2.1. Invoking Superclass Constructors
4.2.2. Calling Superclass Methods
4.3. Polymorphism
4.3.1. Method overloading
4.3.2. Method Overriding
4.4. Abstract Class and method
4.5. Interface
4.6. Overload (method surcharging)
4.7. Modifiers
-
- Write a Java program to create a class called "Shape" with abstract methods for calculating area and perimeter, and subclasses for "Rectangle", "Circle", and "Triangle".
- Write a Java program to create a class called "Person" with a name and age attribute. Create two instances of the "Person" class, set their attributes using the constructor, and print their name and age
- Write a Java program to create a class called "Book" with attributes for title, author, and ISBN, and methods to add and remove books from a collection
- Write a Java program to create a class called "Student" with a name, grade, and courses attributes, and methods to add and remove courses.
-
-
-
5. Integrated Generic data structure in java
5.1.1 Interfaces and implementation
5.1.2. Generic types in Java
5.1.2.1. Set interface
5.1.2.1.1. HashSet
5.1.2.1.2. LinkedHashSet
5.1.2.3. List
5.1.2.3.1 ArrayList
5.1.2.4. Map
5.1.2.5. Queue
5.2. Collection Algorithms
5.2.1. Fill
5.2.3. Sort
5.2.4. Shuffle
5.2.5. Reverse Order
5.2.6. Binary Search
5.3. Collections’ iterating
5.3.1. For-each
5.3.2. Iterator
5.3.3. Massive operations in Java
-
1- Write a Java program to create an array list, add some colors (strings) and print out the collection.
2. Write a Java program to iterate through all elements of this array list.
3. Write a Java program to insert an element into the array list at the first position.
-
-
-
Fichier
6. Graphical API
6.1. Standard Java library API
6.2. Java Natives Interface (JNI)
6.3. AWT and SWINGx library
6.3.1. AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
6.3.2. Swingx
-
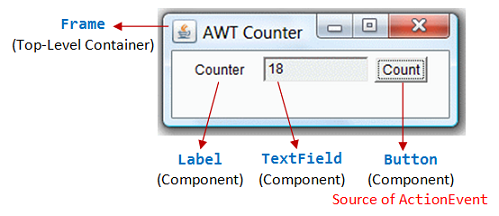
Write an AWT GUI application (called AWT1) as shown in the Figure. Each time the "Count" button is clicked, the counter value shall increase by 1.
The program has three components:- a java.awt.Label "Counter";
- a non-editable java.awt.TextField to display the counter value
- a java.awt.Button "Count".
-
