Tutorials: Elements of chemistry
Topic outline
-
-
Forum
-
-

Subject title: Tutorials:Elements of chemistry
Faculty: Technology
Department: Common Base / Engineering
Cycle: 1st year Engineering
Semester: 1
Credits: 7
Coefficients: 4
Volume: 1h30
Teacher: KAHOUL Fares
Email: fares.kahoul@univ-msila.dz
-

Chemistry is considered an integral part of the history of science and the contemporary world. In general, general chemistry describes the reactivity of elements and their compounds, while providing a broad overview of the principles on which chemistry is based, and is the basis of initial scientific training for chemists. This course contains theoretical developments and uses mathematical tools to understand certain notions of structural chemistry.
-
Chat
-
Feedback
-
-
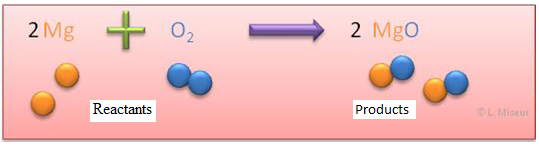
Fundamental concepts
I. Definition of matter
II. Changes of state of matter
III. Classification of matter
IV. Notion of atom, molecule, mole and Avogadro number
V. Law of conservation of mass (Lavoisier), chemical reaction
VI. Qualitative and quantitative aspects of matter
-
Chat
-
Feedback
-
Forum
-
File
-
-
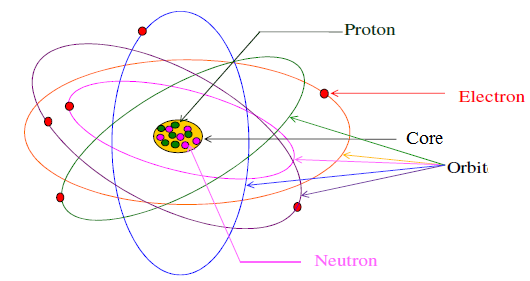
Structure of the atom
I. Electron: Demonstration: J.J. Thomson's experiment, Properties of cathode rays
II. Nucleus: Demonstration: Rutherford experiment, Constitution of the atomic nucleus
III. Element identification: Representation, Atomic mass, Relative atomic mass
-
Chat
-
Feedback
-
Forum
-
File
-
-

Radioactivity
I. Natural radioactivity
II. Artificial radioactivity and nuclear reactions: nuclear fission, nuclear fusion, transmutation
III. Radioactive decay kinetics: radioactive decay law: activity of a radioactive nucleus, radioactive half-life or half-life time
-
Chat
-
Feedback
-
Forum
-
File
-
-
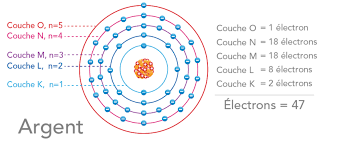
Electronic structure of the atom
I. Production of atomic emission spectra
II. Electromagnetic radiation
III. Photon theory: emission spectrum of the hydrogen atom and the empirical Balmer-Rydberg relation
IV. Classical models of the atom: Rutherford's planetary model and Bohr's model
V. Quantum or wave models of the atom
VI. Schrödinger model and probability of presence
VII. Quantum numbers
VIII. Electronic configuration of atoms and ions
IX. Slater's method for polyelectronic atoms
-
Chat
-
Feedback
-
Forum
-
File
-
-

