TP Chemistry 01 (2023/2024) Groupe GC 01
Topic outline
-
-
Forum
الاختبار في الاسفل
Quiz (Test) TP Chemistry (01)
-
-
-
These practical work sessions are intended for students in the 1st year Common Base. The Chemistry I practical work module consists of five manipulations:
- Manipulation N°1 : General chemistry (Safety and glassware).
- Manipulation N°2 : Preparation of solutions.
- Manipulation N°3 : Titration colorimetric strong acid by strong base.
- Manipulation N°4 : Redox titration.
- Manipulation N°5 : Titration of Vinegar.

Each practical work is accompanied by theoretical information and questions are proposed, in order to control the acquisition and assimilation of knowledge. and Each manipulation is sanctioned by a report given to the teacher within a maximum of 15 days from the date of the manipulation.
TP01
 TP02
TP02 TP03
TP03  TP04
TP04  TP05
TP05
-
Working in a chemical laboratory requires the application of a number of safety rules; these rules are essential for the organisation of work in a laboratory. When you first enter the TP room (laboratory), the student will need to know what to do, how to dress for a TP session (laboratory) , the essential rules for handling materials and chemical products and the commonly used glassware, and how to write up a report.

objectives

- Some general safety rules.
- Some tools and instruments of the chemical laboratory.
ENG
 FR
FR
-
Chat
-
Forum
-
Feedback
-
Accurate volume measurement is of great importance in the laboratory. It can be done using a volumetric or graduated pipette, a graduated burette or a volumetric flask. In this sequence we will show how to prepare or dilute a solution using a volumetric flask to hold a precise volume of liquid.
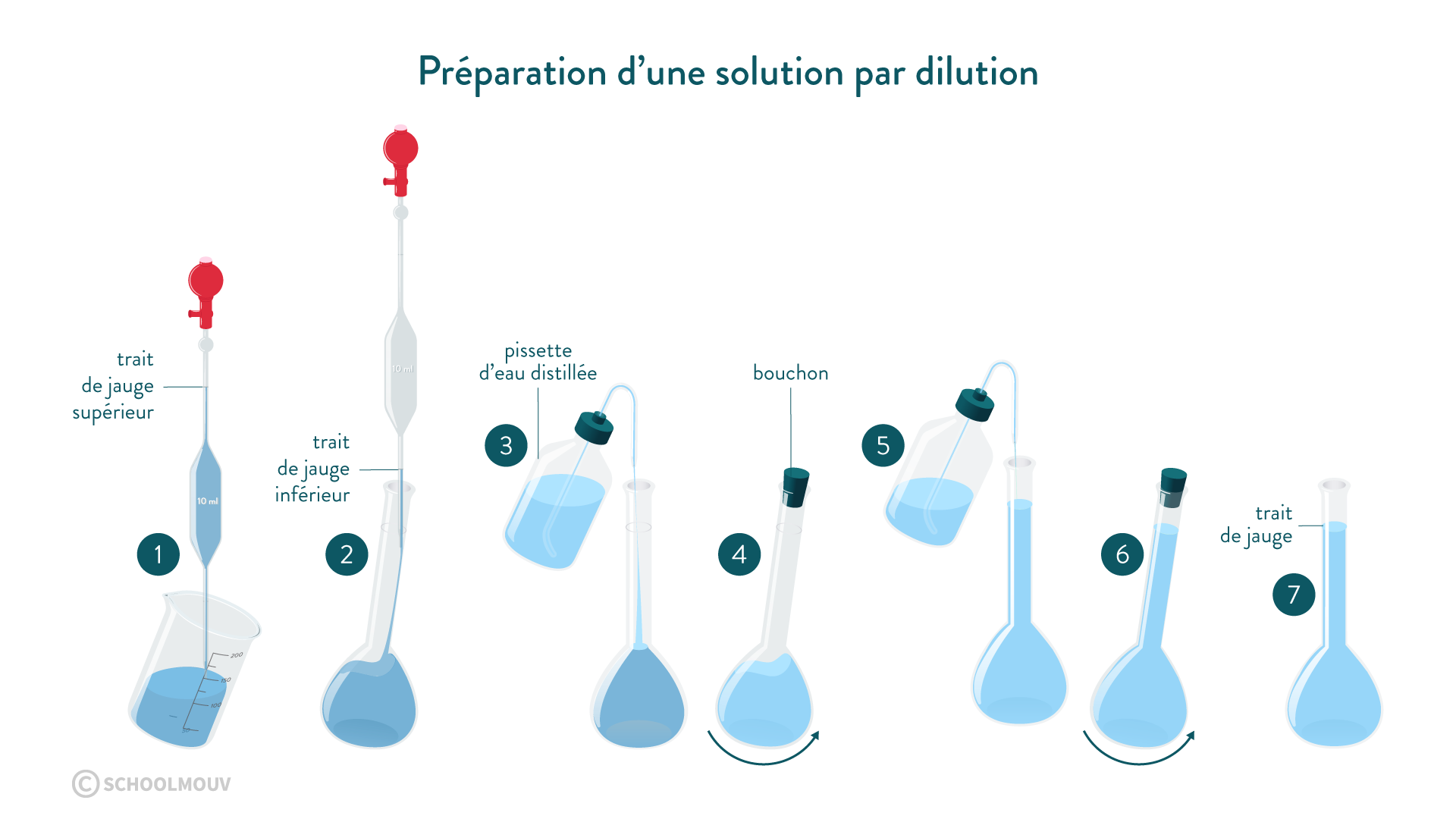
Objectives

- Preparation of a solution by dissolution.
- Preparing a solution by dilution.
ENG
 FR
FR
-
Chat
-
Forum
-
Feedback
-
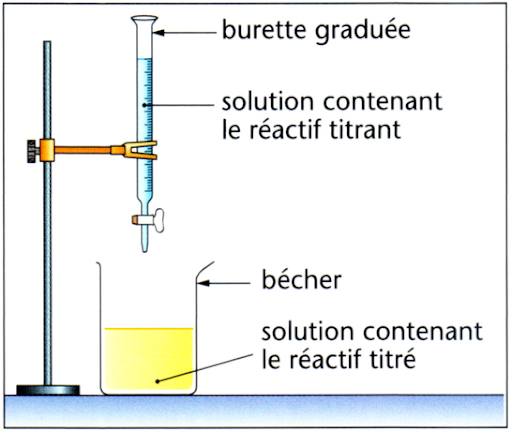
Titrating a solution means determining the concentration of a chemical species A it contains.
To do this, we use a chemical reaction between species A and another chemical species B. The burette contains a solution containing species B, the concentration of which is known precisely and noted CB. The burette is used to measure precisely the volume VB that will be added.
The beaker contains a certain quantity of species A, noted nA. This quantity is unknown, but the volume of solution is known precisely and noted VA.
When a few drops of solution B are added, species B reacts with species A in the beaker.
The species B paid will react as long as there is species A in the beaker. To be able to make a titration :
- The reaction between A and B must be the only reaction that takes place,
- This reaction must be rapid.
- The reaction must be total
When species A has reacted completely with species B, we say that equivalence has been reached. This means that a quantity of substance nB has been added in exactly the stoichiometric proportions given by the equation for the reaction between A and B.
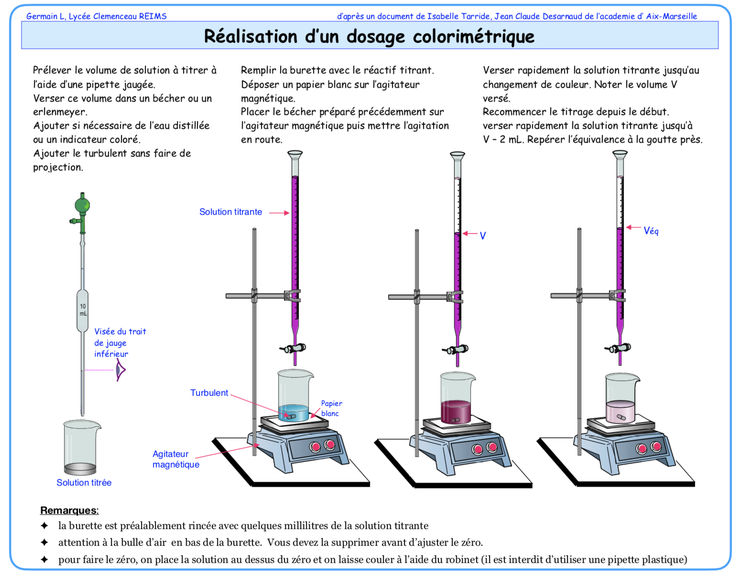
Objectives

hydroxide colorimetric titration of hydrochloric acid by sodium hydroxide.
Draw the graph representing the value of pH= f(VB).
ENG
 FR
FR
-
Chat
-
Forum
-
Feedback
-
Titration involves determining the normality of a reducing solution given the normality of the oxidising solution. We propose to study the oxidation of the Fe2+ ion by the permanganate ion MnO4- in an acid environment.
This titration is called manganometry. Manganimetry is based on the oxidising properties of the permanganate ion. The oxidising form MnO4- is violet, while the reducing form Mn2+is colourless, making it possible to determine the equivalent point without using coloured indicators.
Mn2+
Objectives

Titration of iron in ferrous sulphate with potassium permanganate.
Write down the oxidation-reduction half-reactions and specify the redox couples.
ENG
 FR
FR
-
Chat
-
Forum
-
Feedback
-
Vinegar is a wine (alcohol) made sour by acetic fermentation and used as a condiment or preservative. Vinegar is considered to be an aqueous solution of acetic acid with a density (d) of about 1. The objective of this practical work is to determine the degree of acidity D or (°) of a vinegar, defined as the mass of pure acetic or ethanoic acid contained in 100g of solution. To do this, the acetic (ethanoic) acid contained in a known volume of vinegar will be determined using a strong base solution of known concentration: sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH).

Objectifs

How to control the quality of a product by titration.
Products tested: different types of commercial vinegar.
ENG
 FR
FR
-
Chat
-
Forum
-
Feedback
-
-
-
Opened: Friday, 15 December 2023, 8:00 AMClosed: Friday, 15 December 2023, 6:00 PM
يرجى من الطلبة الافاضل الإجابة على أسئلة الاختبار الموجودة ادناه
* الاختبار متاح ابتداء من يوم الجمعة 15/ 12/ 2023.
* الاختبار يكون من الساعة 8:00 صباحا الى 18:00 مساء.
* مدة الاختبار 20 دقيقة.
* كل طالب لدية فرصة واحدة للإجابة لابد من اغتنامها.
* يرجى مراجعة الاعمال التطبيقية قبل البدأ في الاختبار.
* إضغط على استعراض الاختبار وأبدأ المحاولة



-
