Demonstrate comprehension of the behavior of capacitors in circuits, including charging and discharging processes.
Understand the operation of an oscilloscope, including its controls, probe usage, and waveform display.
Explain the relationship between voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, frequency, and period in electrical circuits.
Applying:
Analyze experimental data to identify patterns and relationships between voltage, current, capacitance, and time during the charging and discharging of a capacitor.
Analyze waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope to identify waveform characteristics and infer properties of the electrical signal being measured.
Evaluate the accuracy and reliability of experimental results obtained during the practical work, considering factors such as experimental error and measurement uncertainty.
Create and present reports summarizing experimental findings, interpretations, and conclusions, demonstrating a synthesis of theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
Practical Work In Physics II/ST/TIC2024/BOUAFIA Saber
Topic outline
-
-
Forum
-
-
-

The purpose of the practical work in Physics for first-year students is to foster a deeper understanding of fundamental concepts through hands-on experimentation to promote various levels of cognitive skills development.By the end of this course, you will :
-
-
-
Chat
-
Forum
-
-
-
Welcome to the world of practical physics II , the electrical part of the module, where theories meet experimentation and classroom concepts come to life in the laboratory. Practical work in physics serves as a crucial bridge between theoretical knowledge and real-world applications, offering you the opportunity to deepen your understanding, sharpen your skills, and cultivate a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the physical world.
Throughout these practical works, you'll engage in a series of practical experiments designed to reinforce key concepts and develop essential problem-solving abilities. From exploring the behavior of capacitors in electrical circuits to mastering the operation of an oscilloscope for waveform analysis, each experiment will challenge you to think critically, analyze data, and draw meaningful conclusions. So, get ready to roll up your sleeves, unleash your curiosity, and embark on a journey of scientific inquiry that will shape your understanding of the fundamental principles of physics and electricity.
-
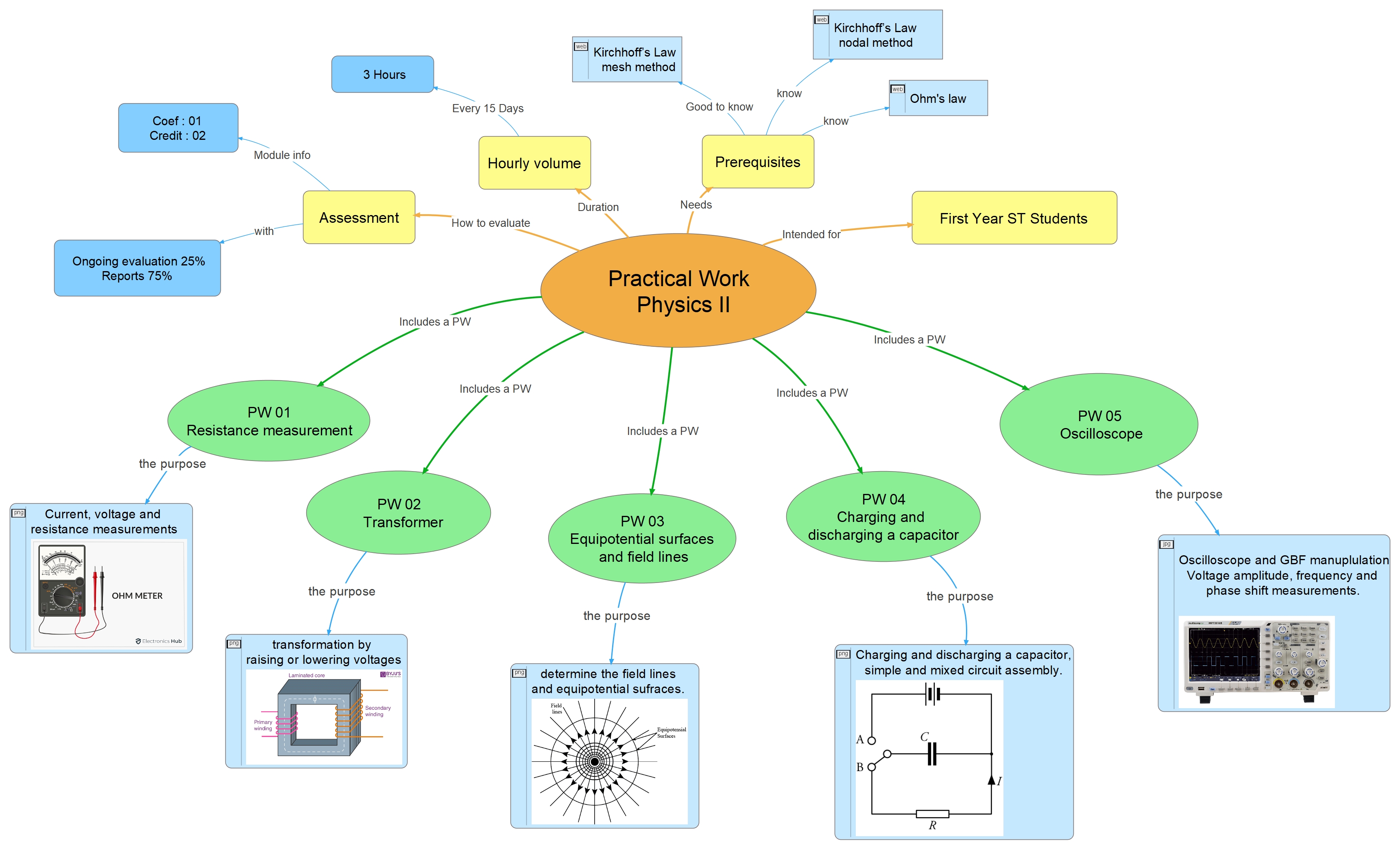
Mind map of the Practical Work in Physics 2 for first-year students.
-
-
-
Before students engage in practical work, it's important they have a foundational understanding of relevant concepts. Here are pre-requests or prior knowledge requirements:
Basic understanding of electricity and circuits: Students should be familiar with the fundamentals of electric circuits, including concepts such as voltage, current, resistance, and Ohm's law.
Knowledge of capacitors: Students should have a basic understanding of capacitors, including their construction, capacitance, and behavior in circuits.
Understanding of waveform characteristics: Students should comprehend different waveform characteristics such as amplitude, frequency, period, and phase, and how these are represented on an oscilloscope.
-
-
-
Introduction

Capacitors are essential components in electrical and electronic circuits, known for their ability to store and release electrical energy. They consist of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric.
When connected to a voltage source, capacitors accumulate charge on their plates, creating an electric field. This stored energy can be released when the circuit demands it, making capacitors crucial for applications like smoothing out voltage fluctuations, powering devices temporarily, and tuning resonant circuits in radios and other electronics. Understanding how capacitors charge and discharge is fundamental to mastering their role in various circuits.
-
By the end of this practical work, the student will be able to :
Recall the fundamental principles and equations related to electricity, circuits, and waveforms learned in theoretical lectures.
Demonstrate comprehension of the behavior of capacitors in circuits, including charging and discharging processes.
Apply the concepts of voltage, current, and resistance to analyze and interpret data collected from capacitor charging and discharging experiments.
Analyze experimental data to identify patterns and relationships between voltage, current, capacitance, and time during the charging and discharging of a capacitor.
-
-
-
Introduction

Oscilloscopes are powerful diagnostic tools used in electronics to visualize electrical signals. They display voltage waveforms on a screen, allowing users to observe signal characteristics such as amplitude, frequency, and period in real-time.
By connecting probes to different points in a circuit, an oscilloscope can help identify signal behaviors and troubleshoot issues. Oscilloscopes are indispensable in fields ranging from telecommunications to automotive engineering, providing insights into the dynamic performance of electronic systems and aiding in the design and maintenance of complex circuitry.
-
By the end of this practical work, the student will be able to :
Remember the procedures for setting up and operating an oscilloscope
Understand the operation of an oscilloscope, including its controls, probe usage, and waveform display.
Apply knowledge of oscilloscope operation to accurately measure and analyze waveforms, including determining amplitude, frequency, and period.
Analyze waveforms displayed on the oscilloscope to identify waveform characteristics and infer properties of the electrical signal being measured.
-
