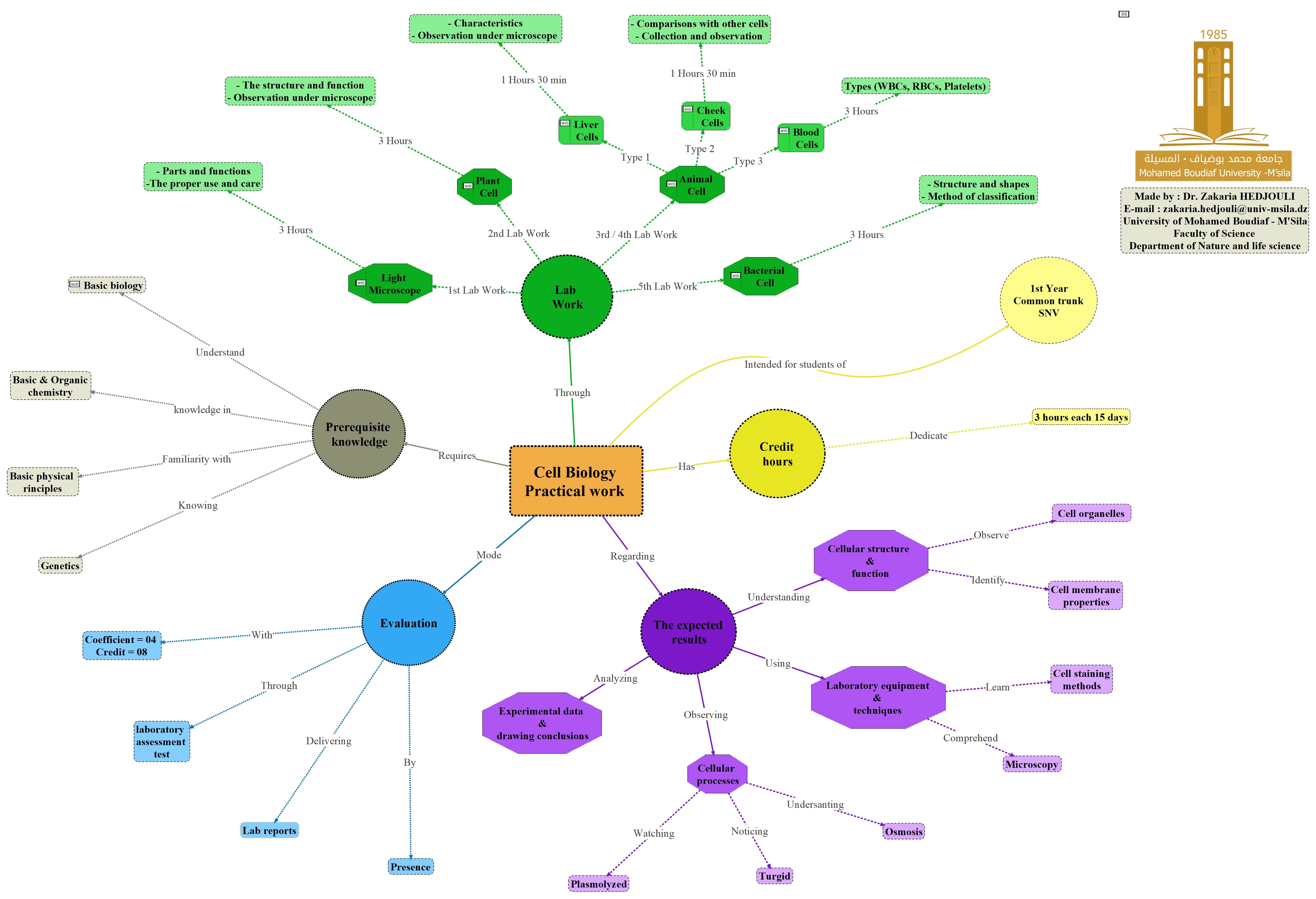
Cellular Biology Laboratory
Topic outline
-
 Faculty: Sciences
Faculty: SciencesDepartment: Common Trunk Nature and Life Sciences
Target audience: 1st year TC license
Course title: Cellular Biology Laboratory (Cell biology Lab)
Credit: 08
Coefficient: 04
Duration: 15 weeks (90h)
Hourly volume: 3h00 Classes – 3h00 Practical work
Evaluation method:
- Continuous assessment: 40%
- Final exam: 60%.
Hourly:
- Sunday: 8:00 a.m. - 11:00 a.m. Amphi: D01
- Monday / Tuesday: 8:00 a.m. - 11:00 a.m. I-20 Lab
-
- Cellular biology laboratory Teacher: Dr. Zakaria HEDJOULI
- Contact : zakaria.hedjouli@univ-msila.dz
- Availability:
- At the teachers' office (D09): Sunday, Monday, Tuesday from 8:30 a.m. to 9:30 a.m.
- Answer on the forum: any question relating to the course must be posted on the dedicated forum so that you can all benefit from my answer, I undertake to answer the questions posted within 48 hours.
- By email:
- I undertake to respond by email within 48 hours following receipt of the message, except in the event of unforeseen circumstances, I draw your attention to the fact that the preferred communication channel is the forum."Note : The email is reserved for "emergencies” (in the event of a problem accessing the platform) and it must be used with discernment."
-
- Objectives
- Introduction
I)- Laboratory safety rules
I.1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
I. 2. General Safety Practices
I. 3. Additional Cautions
II) - 1st Lab work - Compound Light Microscope
II. 1. Objectives of 1st lab work
II. 2. Introduction
II. 3. The different parts of the microscope
II. 3.1. The functions of the different parts of the microscope
II. 4. Principle of a light microscope (optical microscope)
II. 5. Instructions for using the microscope
II. 6. Activity 1
II. 7. Activity 2
II. 7.1. Materials
II. 7.2. Applications
II. 7.3. Observation under the microscope
II. 8. Final Analysis
III) - 2nd Lab work - Microscopic study of Animal cells (Blood smear)
III. 1. Objectives of 2nd lab work
III. 2. Introduction
III. 3. Blood Components
III. 3.1. What is Blood?
III. 3.2. Components of Blood
III. 3.3. Types of White Blood Cells
III. 4. Preparing Blood Smear for observation
III. 4.1. Materials
III. 4.2. Blood Collection
III. 4.3. Staining the Blood Smear
III. 5. Microscope Observation
III. 6. Final Analysis
IV) - Exit test -
-
 Cell biology lab work aims to provide students with hands-on
experience and practical knowledge in various areas related to the
structure, function, and behavior of cells. These labs can be designed to achieve
various objectives, including:
Cell biology lab work aims to provide students with hands-on
experience and practical knowledge in various areas related to the
structure, function, and behavior of cells. These labs can be designed to achieve
various objectives, including:1. Develop practical skills in cell biology techniques: Students will learn and practice essential techniques used in cell biology research and applications.
2. Distinguish the cell biology concepts: Through practical experience, students will solidify their understanding of theoretical concepts learned in lectures.
3. Construct critical thinking and problem-solving skills: encourages students to formulate hypotheses, analyze and interpret data, troubleshoot and adapt procedures.
4. Create scientific communication and collaboration: often involves working in teams, promoting: Collaborating between students and scientific communication.
-

Cell biology (also cellular biology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms.
Cell biology is the study of the structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition.
The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms.
Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such as cancer, and other diseases. Research in cell biology is interconnected to other fields such as genetics, molecular genetics, molecular biology, medical microbiology, and immunology.
-

The student should typically have a strong foundation in biology, chemistry, physics, and sometimes even math to study this module.
Biology: This is the foundation for understanding cell biology. A general biology course will introduce you to the basic concepts of life, including cell structure and function, genetics, and evolution.
Organic Chemistry: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon based molecules, which are the building blocks of life. While not always required, understanding organic chemistry can be helpful for understanding the structure and function of biological molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Physics: provides a foundation for understanding the physical principles that govern cellular processes, such as diffusion, osmosis, and thermodynamics. You'll likely need to cover topics like mechanics, electricity, and magnetism.
Calculus: Although not always required, calculus can be helpful for understanding some of the quantitative aspects of cell biology, such as modeling cellular processes.
-
-
View


Notice :
All Students are invited to test there knowledge before starting this course, to make sure they have the prerequisite needed to study this module.
-
Google Meet™ for Moodle
 - The first meeting with your professor will help you for clarification and guidance
- The first meeting with your professor will help you for clarification and guidance - If you have any questions about the syllabus, course expectations, or challenging concepts
- The first meeting is a perfect opportunity to seek clarification directly from the source. This can help you get off on the right foot and avoid confusion later.
-
-
-

Please check the provided tips
Before starting the lab lesson students should understand the safety rules needed inside the laboratory
" Warning : Anyone not following the rules will be denied access to the lab room "
-
-

1. Alberts, B., Hopkin, K., Johnson, A. D., Morgan, D., Raff M. C., Roberts, K., Walter, P. (2019). Essential Cell Biology. United Kingdom: W.W. Norton. ISBN: 9780393680393
2. Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., & Walter, P. (2002). Molecular biology of the cell, Bruce Alberts...[et al.]. Garland Science. New York. US. ISBN-10: 0-8153-4072-9
3. Kierszenbaum, A.L., Tres, L. (2011). Histology and Cell Biology: An Introduction to Pathology E-Book. United Kingdom: Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN: 9780323683784.
4. Thomas Dean Pollard & William C. Earnshaw, (2004). Biologie cellulaire. Ed. Elsevier Masson, Paris, 853p.
5. Marc Maillet, (2006). Biologie cellulaire. Ed. Elsevier Masson, Paris, 618p.
-
-
Feedback

- We are interested in hearing your opinions on this course.
- We appreciate your feedback & your thoughts.
-