Fluid Mechanics 2
Topic outline
-
-
 Faculté de TechnologieDépartement de Génie MécaniqueModule :MDF2 ( S5 : 2024/2025)Public cible: 3ème Année Licence Génie MécaniqueOption: Energétique
Faculté de TechnologieDépartement de Génie MécaniqueModule :MDF2 ( S5 : 2024/2025)Public cible: 3ème Année Licence Génie MécaniqueOption: EnergétiqueUnité d’enseignement: UEF 3.1.1
Coefficient: 3Crédits: 6
Responsable: Dr: Benkherbache Souad
Email: souad.benkherbache@univ-msila.dz
-

The aim of this course is to provide all the tools you needed to acquire the knowledge and understanding 0f fluid mechanics.
-
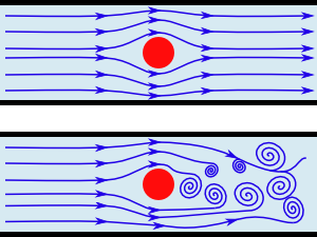
Fluid kinematics, is the analytical description of a system in
in motion. In other words, we are interested in the movements of fluids in relation to time, independently of the causes that cause them.
i.e. without taking taking into account the forces at their source.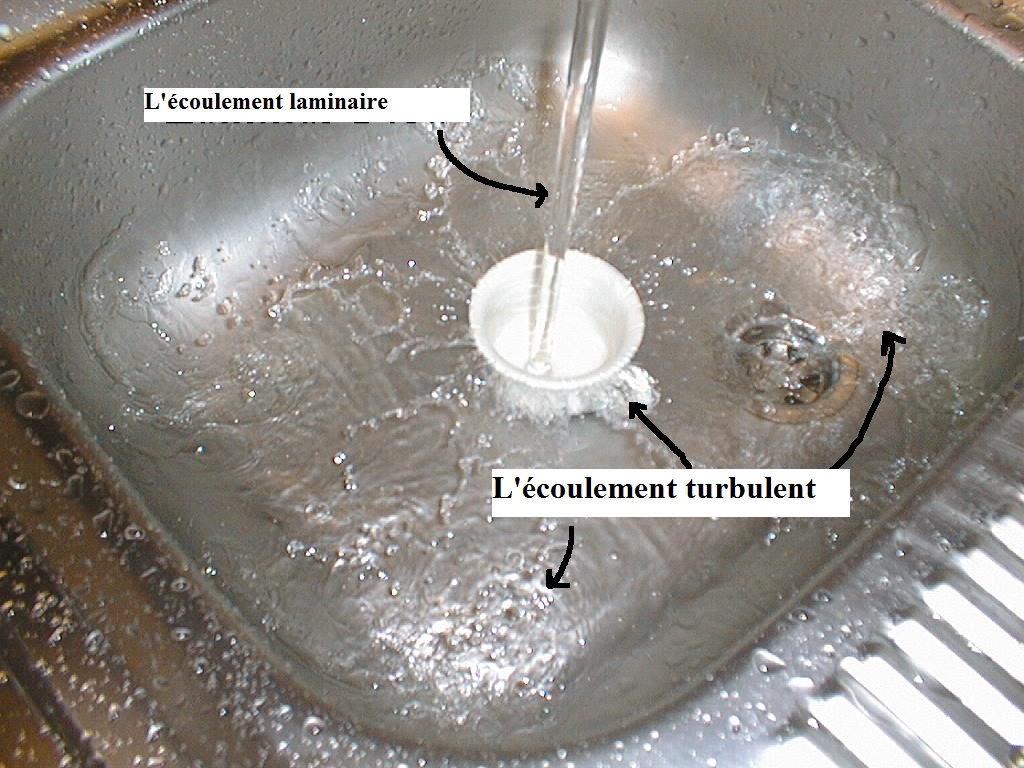
-
Feedback
-
Feedback
-
-
Feedback
-
Forum
-
Chat
-
File
-
File
-
Feedback
-
Forum
-
Chat
-
File
-
File
-
-
In this chapter we will write the balance equations in integral form so that they can be easily understood and solved.
-
In this section, we will apply the Reynolds Transport Theorem (RTT) to:
- Find the conservation equations for mass, momentum and energy.
- Simplify the conservation equations for one-dimensional flow (non-viscous and stationary).
- Analyse the evolution of physical quantities (mass, momentum and energy) using integral balance equations.
-
In this section, we will apply the Reynolds Transport Theorem (RTT) to:
- Find the conservation equations for mass, momentum and energy.
- Simplify the conservation equations for one-dimensional flow (non-viscous and stationary).
- Analyse the evolution of physical quantities (mass, momentum and energy) using integral balance equations.
-
-
Laboratory model Prototype
-
Dimensional analysis is a practical method for checking the homogeneity of a physical formula through its dimensional equations, i.e. the decomposition of the physical quantities it involves into a product of basic quantities: length, duration, mass, electrical intensity, etc., all of which are irreducible.
Dimensional analysis is used to:- Determine the unit of a quantity
- Check the homogeneity of a formula
- Predict the form of a physical law in order to find the solution to certain problems without having to solve an equation: for many of the physical phenomena studied, it is possible to express a characteristic quantity of the phenomenon and deduce an order of magnitude.
-
Dimensional analysis is a practical method for checking the homogeneity of a physical formula through its dimensional equations, i.e. the decomposition of the physical quantities it involves into a product of basic quantities: length, duration, mass, electrical intensity, etc., all of which are irreducible.
Dimensional analysis is used to:- Determine the unit of a quantity
- Check the homogeneity of a formula
- Predict the form of a physical law in order to find the solution to certain problems without having to solve an equation: for many of the physical phenomena studied, it is possible to express a characteristic quantity of the phenomenon and deduce an order of magnitude.
-
